What is Radioberry?
Radioberry is an open-source software-defined radio (SDR) transceiver designed as a “hat” add-on for the Raspberry Pi single-board computer. It enables the Raspberry Pi to function as a fully capable HF (high-frequency) SDR transceiver, covering frequencies from 0 to 30 MHz. The project uses the Analog Devices AD9866 chip and an Intel Cyclone 10 LP FPGA, offering both receive (RX) and transmit (TX) capabilities.
🍓 Radioberry Kit on Amazon ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Whether you’re experimenting with digital modes, learning about RF communication, or building your own low-cost transceiver, Radioberry provides an exciting entry point.
Key Features
- Frequency Coverage: 0–30 MHz (HF bands)
- Architecture: Direct down conversion (DDC) and direct up conversion (DUC) SDR transceiver
- ADC Resolution: 12-bit (via AD9866 chip)
- Channels: 1 RX, 1 TX
- Maximum Bandwidth: Up to 384 kHz
- FPGA: Intel Cyclone 10 LP (supports 10CL16 and 10CL25)
- Form Factor: Raspberry Pi HAT (connects directly to Pi’s GPIO header)
- Power Supply: Powered by the Raspberry Pi
- Open Source: Hardware design, firmware, and software are all freely available for modification and improvement.
How Does Radioberry Work?
Radioberry leverages the processing power and flexibility of the Raspberry Pi, using the Pi as the host for control, user interface, and networking. The HAT handles the RF front-end and digital conversion, while the Pi runs SDR software for operation and visualization. The FPGA is programmed via the Pi, and the radio is controlled through open-source software.
Typical Setup
- Hardware: Raspberry Pi (usually Pi 4), Radioberry HAT, optional touchscreen.
- Software: Raspbian OS, Radioberry firmware, SDR control software.
- Operation: Users can operate the radio locally on the Pi or remotely over a network.
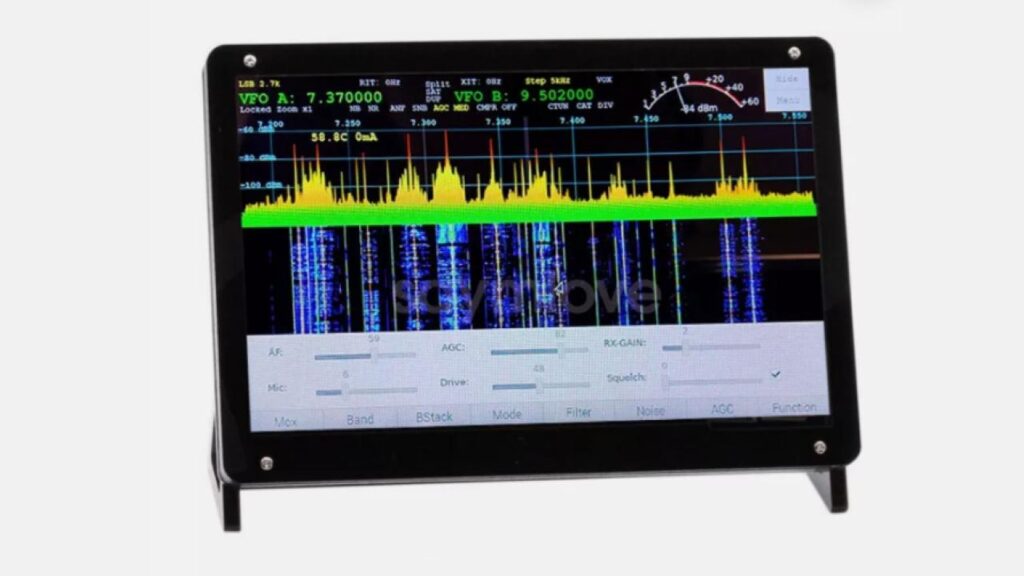
Radioberry with Touch screen
Radioberry version2 features a HF SDR TRANSCEIVER integrated with Raspberry Pi 4B and a 7″ DSI Touch Screen
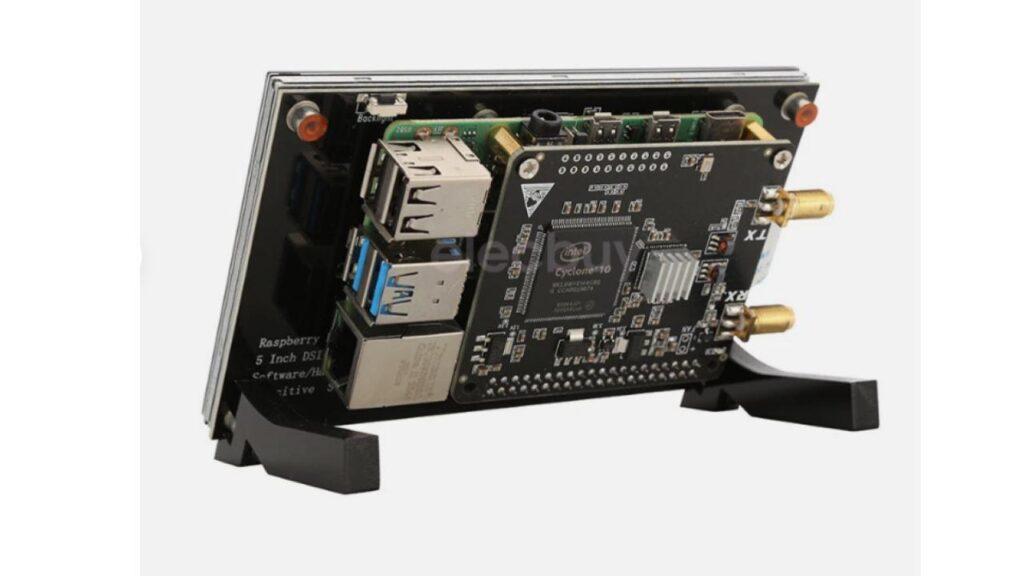

The product comes as an easy to assemble kit: Raspberry pi 4B 1G + radioberry + 7 inch capacitive touch screen + case + tf card with image flashed, you just need to assemble them together.
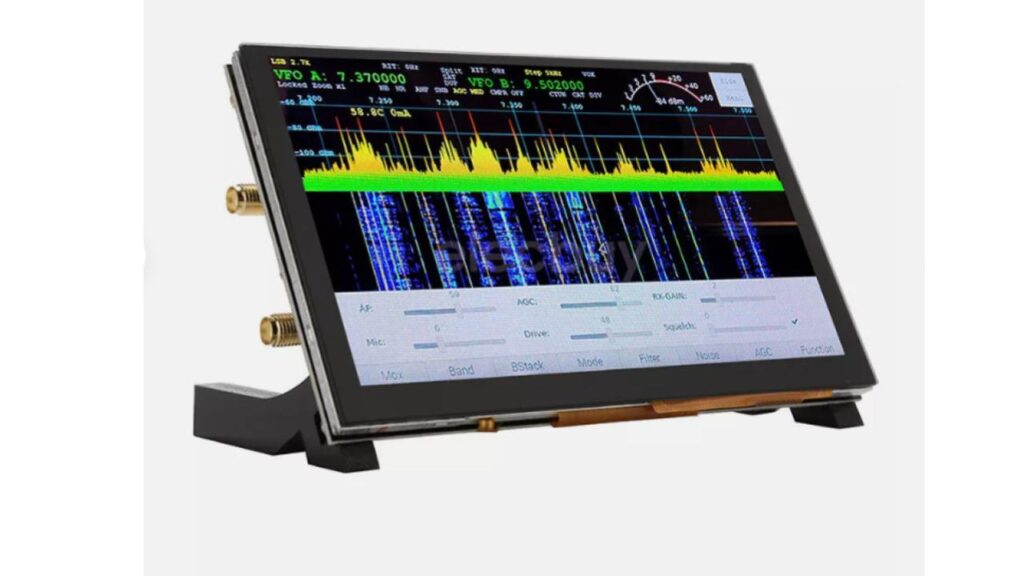
Radioberry Features
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| 🧱 Form Factor | HAT (Hardware Attached on Top) for Raspberry Pi |
| 🧲 Frequency Range | Typically covers 0.1 to 30 MHz (HF) |
| 🔄 Modes | AM, SSB, CW, FM, Digital (FT8, PSK31, etc.) |
| 📡 Transceiver | Both transmit and receive |
| 🧑💻 Software | Compatible with Quisk, Thetis, OpenHPSDR |
| 🔧 DIY Friendly | Open-source hardware and firmware |
How to Use Radioberry with Raspberry Pi
- Install the board on top of a compatible Raspberry Pi (3B, 4, or newer).
- Flash the FPGA firmware onto the board (available on GitHub).
- Install OpenHPSDR-compatible software like Quisk on the Pi.
- Connect an HF antenna.
- Start exploring the airwaves!
🔁 Note: You may need basic Linux knowledge and familiarity with SDR software.
Who Is Radioberry For?
Radioberry is ideal for:
- Amateur radio operators interested in SDR
- Makers and RF tinkerers who love open hardware
- Educational use in DSP, FPGA, and RF learning
- Anyone wanting a compact low-power HF transceiver
🛍️ Where to Buy Radioberry
Radioberry is often sold in limited batches by hobbyist developers or small shops. Look for it on:
Advantages
- Open Source: All hardware, firmware, and software are available for modification and learning.
- Affordable: Lower cost than most commercial SDR transceivers.
- Compact: Small form factor, especially when paired with a Raspberry Pi 4.
- Community Support: Active development and user community, with resources and forums for collaboration.
Limitations
- Output Power: Typically low (e.g., 150 mW), so external amplifiers are needed for higher power applications.
- Availability: Due to component shortages, Radioberry boards can be difficult to source at times, though new production runs do appear.
- Beta Status: The project is considered perpetually in beta, with ongoing improvements and updates.
Software Ecosystem
- PiHPSDR: A desktop SDR control application optimized for use with Radioberry and similar devices.
- Radioberry Juice: User-friendly control software available for multiple platforms.
- SDR Console: Can connect to Radioberry over a local network for remote operation.
Specification Table
| Feature | Radioberry Pi Hat |
|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 0–30 MHz |
| ADC Resolution | 12-bit |
| Max Bandwidth | 384 kHz |
| RX/TX Channels | 1 RX, 1 TX |
| FPGA | Intel Cyclone 10 LP |
| Power | Via Raspberry Pi |
| Software | PiHPSDR, Juice, SDR Console |
| Open Source | Yes |
Community and Reviews
- User Experience: Generally positive, with users praising its flexibility, open-source nature, and suitability for experimentation. Some users note the need for technical skills for assembly and setup.
- Educational Value: Popular in university and research settings for prototyping digital radio modes and SDR applications.
Getting Started
- Obtain a Radioberry board.
- Prepare a Raspberry Pi (Pi 4 recommended).
- Install Raspbian and Radioberry software using available scripts and guides.
- Connect and configure using SDR software.
Conclusion
Radioberry stands out as a powerful, affordable, and open-source SDR solution for HF enthusiasts, educators, and experimenters. Its integration with the Raspberry Pi ecosystem, robust community support, and flexible design make it a unique entry point into the world of software-defined radio.
